Consumer inflation accelerated sharply in November: the NBU named the reasons
Kyiv • UNN
Consumer inflation in November 2024 rose to 11.2%, exceeding the NBU's forecast indicators. The main factors were food and administrative inflation, as well as the rise in prices of non-food goods.

Consumer inflation accelerated rapidly in November 2024 and exceeded the forecast trajectory. This is stated in the macroeconomic and monetary review of the NBU, reports UNN.
Details
"Consumer inflation accelerated rapidly to 11.2% in November and exceeded the trajectory of the forecast published in the Inflation Report for October 2024. The main driver of price growth remained food inflation. Administrative inflation also continued to accelerate", reports the NBU.
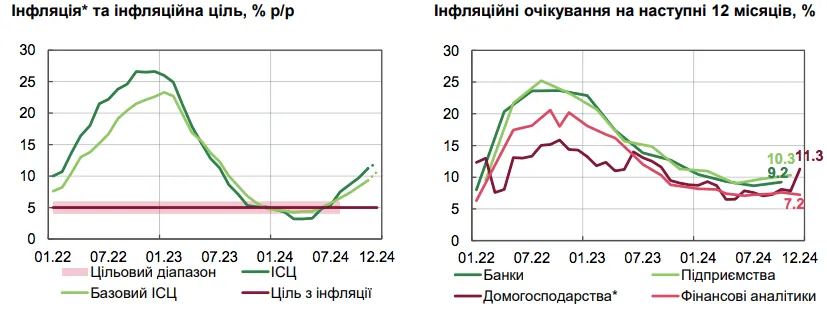
It is noted that core inflation in November rose to 9.3% due to the rapid rise in prices of processed food products, further growth in business costs for energy supply and labor compensation.
The NBU points out that in November, food inflation continued to accelerate rapidly due to lower supply of certain agricultural crops, as well as livestock products, which led to an increase in prices for raw food products.
Prices for non-food goods also accelerated their growth, primarily under the influence of the exchange rate factor. This likely also affected the slowdown in the decline in prices for clothing and footwear. Financial services and communication services, education, culture and recreation, restaurants and hotels, and personal care services became more expensive faster due to increased production costs.
However, in November, there was a slowdown in the growth of fuel prices, which is primarily due to the downward dynamics of global oil prices and the preservation of restrained demand. At the same time, alcoholic and tobacco products became more expensive rapidly, including under the influence of exchange rate effects in previous months and the fight against shadow production.
In addition, the expected increase in excise taxes on tobacco products from January 1, 2025 could also have motivated manufacturers and importers to raise prices in advance. The growth of prices for pharmaceutical products, medical goods and equipment accelerated. As before, administrative inflation was constrained by the moratorium on raising tariffs for certain housing and communal services for the population.
Reminder
The IMF has updated the baseline scenario for Ukraine, forecasting GDP growth of 4% in 2024. The Fund expects the war to end by the end of 2025 and a gradual normalization of economic indicators.