Astronomical events of the summer: how to observe the bright "Summer Triangle" - the star triad Altair, Deneb and Vega
Kyiv • UNN
The bright Summer Triangle, formed by the stars Altair, Deneb and Vega, marks the beginning of summer in the Northern Hemisphere and will be visible in the night sky this week.

This week, a group of bright stars of the Summer Triangle are in the night sky, marking the beginning of summer in the Northern Hemisphere. Live Science tells how to recognize them, reports UNN.
Details
At this time of year, a group of stars called the Summer Triangle rises above the horizon. These are the stars: Vega, Deneba and Altair. Their appearance in the night sky signals the beginning of summer in the Northern Hemisphere and winter in the Southern Hemisphere (where it is known as the Winter Triangle). In addition, this triangle of bright stars indicates where to look for the Milky Way (a silver-white hazy streak formed by the light of a huge number of stars in our galaxy - ed.
With the onset of summer, all three stars will be visible in the night sky. You don't need to use binoculars to see the Summer Triangle, but a telescope will certainly be helpful.
Vega will appear in the east - it is a large star located 25 light-years from the solar system After tuning in to Vega, you can move northeast and see the double star Epsilon Lyrae. As you move northeast, Altair, the twelfth brightest star in the sky, 17 light-years away, will appear below and to the right on the horizon. Like Vega, Altair is about twice the mass and radius of the Sun.
First black astronaut finally reaches space after 63 years of waiting20.05.24, 16:07 • 118765 views
Finally, to complete the triangle, you need to find Deneb, which can be seen if you look a little lower, in the southwest direction. It is a supergiant, the 19th brightest star. Deneb is much further away than Vega and Altair, at a distance of 2600 light years; the supergiant star is 20 times more massive and about 200 times larger in radius than our Sun.
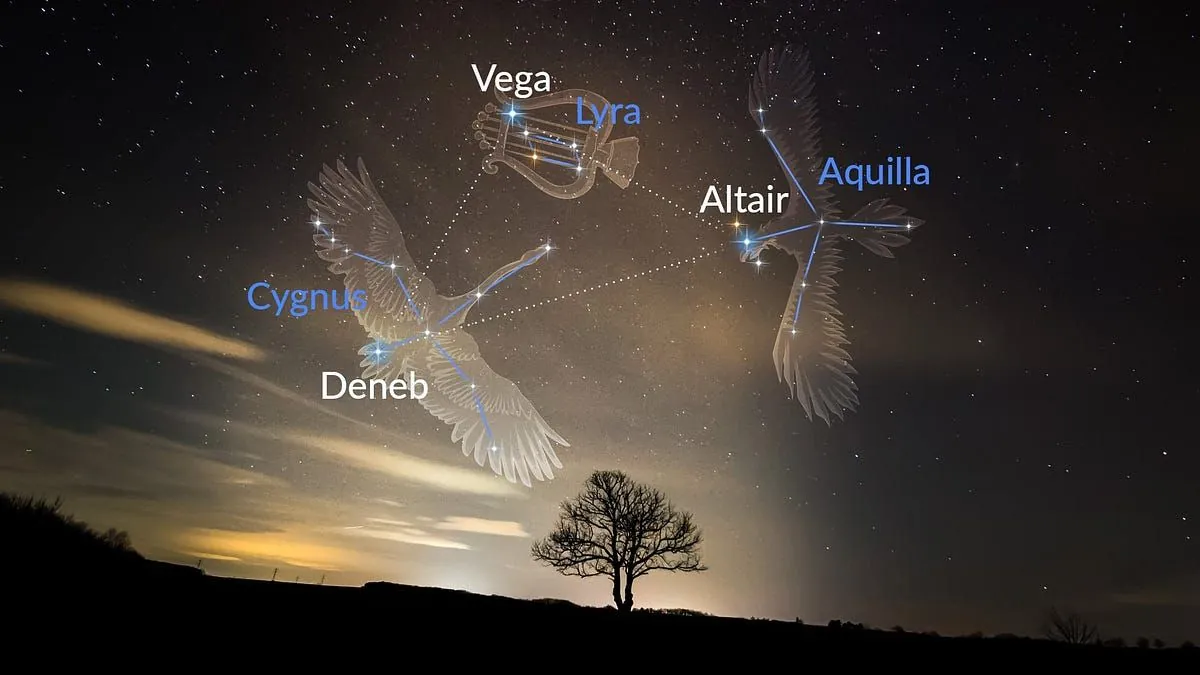
The Summer Triangle is worth finding and observing throughout the summer as it rises higher into the sky each night. It crosses the rich field of the Milky Way, so if you're in a dark sky park or other place with low light pollution, look for the Summer Triangle and you'll see the Milky Way passing through it, from Deneb to Altair," the Live Science article says.